Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| CBFB |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1CL3, 1E50, 1H9D, 4N9F |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | CBFB, PEBP2B, core-binding factor, beta subunit, core-binding factor beta subunit, core-binding factor subunit beta |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 121360; MGI: 99851; HomoloGene: 11173; GeneCards: CBFB; OMA:CBFB - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 16 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 16q22.1 | Start | 67,028,984 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 67,101,058 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 8 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 8 D3|8 53.04 cM | Start | 105,897,306 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 105,944,621 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - secondary oocyte
- sural nerve
- tibia
- Achilles tendon
- periodontal fiber
- tibialis anterior muscle
- cartilage tissue
- bone marrow cells
- islet of Langerhans
- Epithelium of choroid plexus
|
| | Top expressed in | - trigeminal ganglion
- calvaria
- triceps brachii muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
- quadriceps femoris muscle
- extensor digitorum longus muscle
- temporal muscle
- vastus lateralis muscle
- plantaris muscle
- body of femur
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 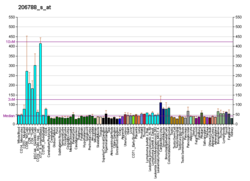
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- transcription coactivator activity
- protein binding
- DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- transcription coregulator activity
- sequence-specific DNA binding
| | Cellular component | - nucleus
- membrane
- nucleoplasm
- core-binding factor complex
| | Biological process | - definitive hemopoiesis
- myeloid cell differentiation
- protein polyubiquitination
- cell maturation
- transcription by RNA polymerase II
- ossification
- osteoblast differentiation
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- lymphocyte differentiation
- regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway
- regulation of Wnt signaling pathway
- regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway
- regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation
- regulation of keratinocyte differentiation
- regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
- regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation
- regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway
- regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation
- regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly
- transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation
- positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001755
NM_022845
NM_001368707
NM_001368708
NM_001368709
|
|---|
NM_001368710 |
| |
|---|
NM_001161456
NM_001161457
NM_001161458
NM_022309 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001746
NP_074036
NP_001355636
NP_001355637
NP_001355638
|
|---|
NP_001355639 |
| |
|---|
NP_001154928
NP_001154929
NP_001154930
NP_071704 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 16: 67.03 – 67.1 Mb | Chr 8: 105.9 – 105.94 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Core-binding factor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CBFB gene.[5][6]
The protein encoded by this gene is the beta subunit of a heterodimeric core-binding transcription factor belonging to the PEBP2/CBF transcription factor family which master-regulates a host of genes specific to hematopoiesis (e.g., RUNX1) and osteogenesis (e.g., RUNX2). The beta subunit is a non-DNA binding regulatory subunit; it allosterically enhances DNA binding by the alpha subunit as the complex binds to the core site of various enhancers and promoters, including murine leukemia virus, polyomavirus enhancer, T-cell receptor enhancers and GM-CSF promoters. Alternative splicing generates two mRNA variants, each encoding a distinct carboxyl terminus. In some cases, a pericentric inversion of chromosome 16 [inv(16)(p13q22)] produces a chimeric transcript consisting of the N terminus of core-binding factor beta in a fusion with the C-terminal portion of the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain 11. This chromosomal rearrangement is associated with acute myeloid leukemia of the M4Eo subtype. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[7]
Mutations in CBFB are implicated in cases of breast cancer.[8]
Core binding factor acute myeloid leukaemia is a cancer related to genetic changes in the CBF gene. It is most commonly caused by an inversion of particular region of chromosome 16; however it can also be caused by translocation between copies of chromosome 16. The rearrangements cause formation of CBF but with impaired function. This prevents proper differentiation of blood cells, leading to the formation of Myeloblast.[9]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000067955 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031885 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Liu P, Tarle SA, Hajra A, Claxton DF, Marlton P, Freedman M, Siciliano MJ, Collins FS (Sep 1993). "Fusion between transcription factor CBF beta/PEBP2 beta and a myosin heavy chain in acute myeloid leukemia". Science. 261 (5124) (published 20 August 1993): 1041–4. Bibcode:1993Sci...261.1041L. doi:10.1126/science.8351518. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 8351518. S2CID 13278253. Wikidata Q24311601.
- ^ Liu P, Seidel N, Bodine D, Speck N, Tarle S, Collins FS (Nov 1995). "Acute myeloid leukemia with Inv (16) produces a chimeric transcription factor with a myosin heavy chain tail". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 59: 547–53. doi:10.1101/sqb.1994.059.01.061. PMID 7587111.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CBFB core-binding factor, beta subunit".
- ^ The Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2012). "Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours". Nature. 490 (7418). Nature Publishing Group: 61–70. Bibcode:2012Natur.490...61T. doi:10.1038/nature11412. PMC 3465532. PMID 23000897.
- ^ "CBFB Gene." Genetics Home Reference. US National Library of Medicine, 10 Sept. 2015. Web. 27 Sept. 2015.
External links
Further reading
- Hart SM, Foroni L (2003). "Core binding factor genes and human leukemia". Haematologica. 87 (12): 1307–23. PMID 12495904.
- Bae SC, Takahashi E, Zhang YW, et al. (1995). "Cloning, mapping and expression of PEBP2 alpha C, a third gene encoding the mammalian Runt domain". Gene. 159 (2): 245–8. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00060-J. PMID 7622058.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Hillier LD, Lennon G, Becker M, et al. (1997). "Generation and analysis of 280,000 human expressed sequence tags". Genome Res. 6 (9): 807–28. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.807. PMID 8889549.
- Hajra A, Collins FS (1 November 1996). "Retraction: Structure of the Leukemia-Associated Human CBFB Gene". Genomics (in English and English). 38 (1): 107. doi:10.1006/GENO.1996.0603. ISSN 0888-7543. PMID 9064279. Wikidata Q56607463.
- Chiba N, Watanabe T, Nomura S, et al. (1997). "Differentiation dependent expression and distinct subcellular localization of the protooncogene product, PEBP2beta/CBFbeta, in muscle development". Oncogene. 14 (21): 2543–52. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201109. PMID 9191054.
- Tanaka Y, Watanabe T, Chiba N, et al. (1997). "The protooncogene product, PEBP2beta/CBFbeta, is mainly located in the cytoplasm and has an affinity with cytoskeletal structures". Oncogene. 15 (6): 677–83. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201235. PMID 9264408. S2CID 7192875.
- Kitabayashi I, Ida K, Morohoshi F, et al. (1998). "The AML1-MTG8 leukemic fusion protein forms a complex with a novel member of the MTG8(ETO/CDR) family, MTGR1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (2): 846–58. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.2.846. PMC 108796. PMID 9447981.
- Levanon D, Goldstein RE, Bernstein Y, et al. (1998). "Transcriptional repression by AML1 and LEF-1 is mediated by the TLE/Groucho corepressors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (20): 11590–5. Bibcode:1998PNAS...9511590L. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.20.11590. PMC 21685. PMID 9751710.
- Kogan SC, Lagasse E, Atwater S, et al. (1998). "The PEBP2betaMYH11 fusion created by Inv(16)(p13;q22) in myeloid leukemia impairs neutrophil maturation and contributes to granulocytic dysplasia". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (20): 11863–8. Bibcode:1998PNAS...9511863K. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.20.11863. PMC 21731. PMID 9751756.
- Goger M, Gupta V, Kim WY, et al. (1999). "Molecular insights into PEBP2/CBF beta-SMMHC associated acute leukemia revealed from the structure of PEBP2/CBF beta". Nat. Struct. Biol. 6 (7): 620–3. doi:10.1038/10664. PMID 10404215. S2CID 13114284.
- Lutterbach B, Hou Y, Durst KL, Hiebert SW (1999). "The inv(16) encodes an acute myeloid leukemia 1 transcriptional corepressor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (22): 12822–7. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9612822L. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.22.12822. PMC 23113. PMID 10536006.
- Warren AJ, Bravo J, Williams RL, Rabbitts TH (2000). "Structural basis for the heterodimeric interaction between the acute leukaemia-associated transcription factors AML1 and CBFbeta". The EMBO Journal. 19 (12): 3004–15. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.12.3004. PMC 203359. PMID 10856244.
- Kanto S, Chiba N, Tanaka Y, et al. (2000). "The PEBP2beta/CBF beta-SMMHC chimeric protein is localized both in the cell membrane and nuclear subfractions of leukemic cells carrying chromosomal inversion 16". Leukemia. 14 (7): 1253–9. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2401821. PMID 10914550. S2CID 22471555.
- O'Reilly J, Chipper L, Springall F, Herrmann R (2000). "A unique structural abnormality of chromosome 16 resulting in a CBF beta-MYH11 fusion transcript in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia, FAB M4". Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 121 (1): 52–5. doi:10.1016/S0165-4608(00)00235-1. PMID 10958941.
- Bravo J, Li Z, Speck NA, Warren AJ (2001). "The leukemia-associated AML1 (Runx1)--CBF beta complex functions as a DNA-induced molecular clamp". Nat. Struct. Biol. 8 (4): 371–8. doi:10.1038/86264. PMID 11276260. S2CID 23570097.
- Bäckström S, Wolf-Watz M, Grundström C, et al. (2002). "The RUNX1 Runt domain at 1.25A resolution: a structural switch and specifically bound chloride ions modulate DNA binding". J. Mol. Biol. 322 (2): 259–72. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00702-7. PMID 12217689.
PDB gallery
-
1cl3: MOLECULAR INSIGHTS INTO PEBP2/CBF-SMMHC ASSOCIATED ACUTE LEUKEMIA REVEALED FROM THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF PEBP2/CBF BETA -
1e50: AML1/CBF COMPLEX -
1h9d: AML1/CBF-BETA/DNA COMPLEX -
1ilf: NMR STRUCTURE OF APO CBFB -
1io4: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RUNX-1/AML1/CBFALPHA RUNT DOMAIN-CBFBETA CORE DOMAIN HETERODIMER AND C/EBPBETA BZIP HOMODIMER BOUND TO A DNA FRAGMENT FROM THE CSF-1R PROMOTER -
2jhb: CORE BINDING FACTOR BETA |
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 16 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

 1cl3: MOLECULAR INSIGHTS INTO PEBP2/CBF-SMMHC ASSOCIATED ACUTE LEUKEMIA REVEALED FROM THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF PEBP2/CBF BETA
1cl3: MOLECULAR INSIGHTS INTO PEBP2/CBF-SMMHC ASSOCIATED ACUTE LEUKEMIA REVEALED FROM THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF PEBP2/CBF BETA 1e50: AML1/CBF COMPLEX
1e50: AML1/CBF COMPLEX 1h9d: AML1/CBF-BETA/DNA COMPLEX
1h9d: AML1/CBF-BETA/DNA COMPLEX 1ilf: NMR STRUCTURE OF APO CBFB
1ilf: NMR STRUCTURE OF APO CBFB 1io4: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RUNX-1/AML1/CBFALPHA RUNT DOMAIN-CBFBETA CORE DOMAIN HETERODIMER AND C/EBPBETA BZIP HOMODIMER BOUND TO A DNA FRAGMENT FROM THE CSF-1R PROMOTER
1io4: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RUNX-1/AML1/CBFALPHA RUNT DOMAIN-CBFBETA CORE DOMAIN HETERODIMER AND C/EBPBETA BZIP HOMODIMER BOUND TO A DNA FRAGMENT FROM THE CSF-1R PROMOTER 2jhb: CORE BINDING FACTOR BETA
2jhb: CORE BINDING FACTOR BETA























