Platinum tetrafluoride
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Platinum(IV) fluoride | |
| Other names Platinum tetrafluoride Platinous fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | F4Pt |
| Molar mass | 271.078[1] |
| Appearance | red-orange solid[1] |
| Density | 7.08 g/cm3 (calc.)[2] |
| Melting point | 600 °C (1,112 °F; 873 K)[1] |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | +455.0·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Structure | |
Crystal structure | Orthorhombic, oF40 |
Space group | Fdd2, No. 43[2] |
Lattice constant | a = 0.9284 nm, b = 0.959 nm, c = 0.5712 nm |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Platinum(IV) bromide Platinum(IV) chloride |
Related compounds | Platinum(V) fluoride Platinum(VI) fluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
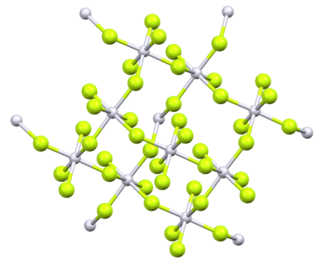
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.[2]
Preparation
The compound was first reported by Henri Moissan by the fluorination of platinum metal in the presence of hydrogen fluoride.[3] A modern synthesis involves thermal decomposition of platinum hexafluoride.[4]
Properties
Platinum tetrafluoride vapour at 298.15 K consists of individual molecules. The enthalpy of sublimation is 210 kJmol−1.[5] Original analysis of powdered PtF4 suggested a tetrahedral molecular geometry, but later analysis by several methods identified it as octahedral, with four of the six fluorines on each platinum bridging to adjacent platinum centres.[6]
Reactions
A solution of platinum tetrafluoride in water is coloured reddish brown, but it rapidly decomposes, releasing heat and forming an orange coloured platinum dioxide hydrate precipitate and fluoroplatinic acid.[7] When heated to a red hot temperature, platinum tetrafluoride decomposes to platinum metal and fluorine gas. When heated in contact with glass, silicon tetrafluoride gas is produced along with the metal.[7]
Platinum tetrafluoride can form adducts with selenium tetrafluoride and bromine trifluoride.[7] Volatile crystalline adducts are also formed in combination with BF3, PF3, BCl3, and PCl3.[7]
Related compounds
The fluoroplatinates are salts containing the PtF62− ion. Fluoroplatinic acid H2PtF6 forms yellow crystals that absorb water from the air. Ammonium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, and rare earth including lanthanum fluoropalatinate salts are soluble in water.[7] Potassium, rubidium, caesium, and barium salts are insoluble in water.[7]
References
- ^ a b c Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.81. ISBN 1-4398-5511-0.
- ^ a b c Mueller, B. G.; Serafin, M. (1992). "Single-crystal investigations on PtF4 and PtF5". European Journal of Solid State Inorganic Chemistry. 29: 625–633. doi:10.1002/chin.199245006.[full citation needed]
- ^ Moissan, H. "Platinum tetrafluoride". Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences. 109: 807–9.
- ^ Slivnik, J. E.; Z̆emva, B.; Druz̆ina, B. (1980). "New syntheses of platinum (IV) and platinum (VI) fluorides". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 15 (4): 351. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81471-2.
- ^ Bondarenko, A.A; Korobov, M.V; Mitkin, V.N; Sidorov, L.N (March 1988). "Enthalpy of sublimation of platinum tetrafluoride". The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 20 (3): 299–303. doi:10.1016/0021-9614(88)90125-5.
- ^ "Solid State Structures of the Binary Fluorides of the Transition Metals". Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry. Vol. 27. Academic Press. 1983. Section V: Tetrafluorides, pages 97–103. ISBN 9780080578767.
- ^ a b c d e f Derek Harry Lohmann (October 1961). The fluorides of platinum and related compounds (Thesis). University of British Columbia.
- v
- t
- e
- Cs2Pt
- Pt(PPh3)4
- Pt(NH3)2(CO2)2C4H6
- cis-Pt(NH3)2Cl2
- trans-Pt(NH3)2Cl2
- K2Pt(CN)4
- Pt(NH3)4PtCl4
- Pt(NH3)2CO2CH2O
- (Cy(NH2)2)PtC2O4
- NH3PtCl2(PyrMe)
- Pt(OAc)2
- PtBr2
- PtCl2
- PtF2
- PtI
2 - PtP2
- K2PtCl4
- [(PtCl(NH3)2(C6H12(NH2)2))Pt(NH3)2](NO3)4
- Pt(OH)2
- PtSm
- Pt(C5H7O2)2
- PtS
| Organoplatinum(II) compounds |
|---|
- PtO2
- (NH4)2PtCl6
- H2PtCl6
- PtBr4
- PtCl4
- PtF4
- K2PtCl6
- Pt(OAc)2Cl2(NH3)(NH2Cy)
- Na2PtCl6
- Pt(OH)4
- PtI4
- PtS2
- PtSe2
- PtF5
- O2PtF6
- XePtF6
- PtF6












