U2AF2
| U2AF2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | U2AF2, U2AF65, U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 191318; MGI: 98886; HomoloGene: 110853; GeneCards: U2AF2; OMA:U2AF2 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Splicing factor U2AF 65 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the U2AF2 gene.[5]
Function
In eukaryotes, the introns in the transcribed pre-mRNA first have to be removed by spliceosome in order to form a mature mRNA. A spliceosome is assembled from small nuclear ribonucleoproteins(snRNP) and small nuclear RNAs(snRNA). And the splicing factor can be divided into snRNP and non snRNP proteins.U2 auxiliary factor (U2AF), composed of a large and a small subunit, is a non-snRNP protein required for the binding of U2 snRNP to the pre-mRNA branch site. This gene encodes the U2AF large subunit, which contains a sequence-specific RNA-binding region with 3 RNA recognition motifs and an Arg/Ser-rich domain necessary for splicing. The large subunit binds to the polypyrimidine tract of introns early during spliceosome assembly. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been detected for this gene, but the full-length natures of only two have been determined to date.[6]
In humans and other tetrapods, it has been shown that without U2AF2, the splicing process is inhibited. However, in zebrafish and other teleosts the RNA splicing process can still occur on certain genes in the absence of U2AF2. This may be because 10% of genes have alternating TG and AC base pairs at the 3' splice site (3'ss) and 5' splice site (5'ss) respectively on each intron, which alters the secondary structure of the RNA and influences splicing.[7]
The splicing factor U2AF65 can specifically recognizes the polypyrimidine tract (Py tract), that’s because U2AF65 consists of 3 RNA binding domains (RRMs), all of them have a high binding affinity to the Py tract on its adjacent 3’ splice site.[6] The RRM1 and RRM2 are sufficient for specific RNA/protein binding, while RRM3 is responsible for protein/protein interactions. For example, the C-Terminal RRM3 contribute to establish protein–protein contacts with splicing factors like UAP56, SAP155, and mBBP/SF1.[8]
Interactions
U2AF2 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000063244 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030435 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Zamore PD, Patton JG, Green MR (February 1992). "Cloning and domain structure of the mammalian splicing factor U2AF". Nature. 355 (6361): 609–614. Bibcode:1992Natur.355..609Z. doi:10.1038/355609a0. PMID 1538748. S2CID 4332390.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: U2AF2 U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 2".
- ^ Lin CL, Taggart AJ, Lim KH, Cygan KJ, Ferraris L, Creton R, et al. (January 2016). "RNA structure replaces the need for U2AF2 in splicing". Genome Research. 26 (1): 12–23. doi:10.1101/gr.181008.114. PMC 4691745. PMID 26566657.
- ^ Selenko P, Gregorovic G, Sprangers R, Stier G, Rhani Z, Krämer A, Sattler M (April 2003). "Structural basis for the molecular recognition between human splicing factors U2AF65 and SF1/mBBP". Molecular Cell. 11 (4): 965–976. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00115-1. PMID 12718882.
- ^ a b c d Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, et al. (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–1178. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- ^ Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Molecular Systems Biology. 3: 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
- ^ Berglund JA, Abovich N, Rosbash M (March 1998). "A cooperative interaction between U2AF65 and mBBP/SF1 facilitates branchpoint region recognition". Genes & Development. 12 (6): 858–867. doi:10.1101/gad.12.6.858. PMC 316625. PMID 9512519.
- ^ Abovich N, Rosbash M (May 1997). "Cross-intron bridging interactions in the yeast commitment complex are conserved in mammals". Cell. 89 (3): 403–412. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80221-4. PMID 9150140. S2CID 18466775.
- ^ Zhang WJ, Wu JY (October 1996). "Functional properties of p54, a novel SR protein active in constitutive and alternative splicing". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 16 (10): 5400–5408. doi:10.1128/MCB.16.10.5400. PMC 231539. PMID 8816452.
- ^ Zhang WJ, Wu JY (February 1998). "Sip1, a novel RS domain-containing protein essential for pre-mRNA splicing". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (2): 676–684. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.2.676. PMC 108778. PMID 9447963.
- ^ Wang HY, Lin W, Dyck JA, Yeakley JM, Songyang Z, Cantley LC, Fu XD (February 1998). "SRPK2: a differentially expressed SR protein-specific kinase involved in mediating the interaction and localization of pre-mRNA splicing factors in mammalian cells". The Journal of Cell Biology. 140 (4): 737–750. doi:10.1083/jcb.140.4.737. PMC 2141757. PMID 9472028.
- ^ Zhang M, Zamore PD, Carmo-Fonseca M, Lamond AI, Green MR (September 1992). "Cloning and intracellular localization of the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor small subunit". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 89 (18): 8769–8773. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.8769Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.18.8769. PMC 50002. PMID 1388271.
- ^ Davies RC, Calvio C, Bratt E, Larsson SH, Lamond AI, Hastie ND (October 1998). "WT1 interacts with the splicing factor U2AF65 in an isoform-dependent manner and can be incorporated into spliceosomes". Genes & Development. 12 (20): 3217–3225. doi:10.1101/gad.12.20.3217. PMC 317218. PMID 9784496.
Further reading
- Zhang M, Zamore PD, Carmo-Fonseca M, Lamond AI, Green MR (September 1992). "Cloning and intracellular localization of the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor small subunit". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 89 (18): 8769–8773. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.8769Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.18.8769. PMC 50002. PMID 1388271.
- Zamore PD, Green MR (January 1991). "Biochemical characterization of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor: an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor with a novel intranuclear distribution". The EMBO Journal. 10 (1): 207–214. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07937.x. PMC 452631. PMID 1824937.
- Zuo P, Maniatis T (June 1996). "The splicing factor U2AF35 mediates critical protein-protein interactions in constitutive and enhancer-dependent splicing". Genes & Development. 10 (11): 1356–1368. doi:10.1101/gad.10.11.1356. PMID 8647433.
- Zhang WJ, Wu JY (October 1996). "Functional properties of p54, a novel SR protein active in constitutive and alternative splicing". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 16 (10): 5400–5408. doi:10.1128/MCB.16.10.5400. PMC 231539. PMID 8816452.
- Hong W, Bennett M, Xiao Y, Feld Kramer R, Wang C, Reed R (January 1997). "Association of U2 snRNP with the spliceosomal complex E". Nucleic Acids Research. 25 (2): 354–361. doi:10.1093/nar/25.2.354. PMC 146436. PMID 9016565.
- Abovich N, Rosbash M (May 1997). "Cross-intron bridging interactions in the yeast commitment complex are conserved in mammals". Cell. 89 (3): 403–412. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80221-4. PMID 9150140. S2CID 18466775.
- Tronchère H, Wang J, Fu XD (July 1997). "A protein related to splicing factor U2AF35 that interacts with U2AF65 and SR proteins in splicing of pre-mRNA". Nature. 388 (6640): 397–400. Bibcode:1997Natur.388..397T. doi:10.1038/41137. PMID 9237760. S2CID 4386808.
- Fleckner J, Zhang M, Valcárcel J, Green MR (July 1997). "U2AF65 recruits a novel human DEAD box protein required for the U2 snRNP-branchpoint interaction". Genes & Development. 11 (14): 1864–1872. doi:10.1101/gad.11.14.1864. PMID 9242493.
- Zhang WJ, Wu JY (February 1998). "Sip1, a novel RS domain-containing protein essential for pre-mRNA splicing". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (2): 676–684. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.2.676. PMC 108778. PMID 9447963.
- Wang HY, Lin W, Dyck JA, Yeakley JM, Songyang Z, Cantley LC, Fu XD (February 1998). "SRPK2: a differentially expressed SR protein-specific kinase involved in mediating the interaction and localization of pre-mRNA splicing factors in mammalian cells". The Journal of Cell Biology. 140 (4): 737–750. doi:10.1083/jcb.140.4.737. PMC 2141757. PMID 9472028.
- Berglund JA, Abovich N, Rosbash M (March 1998). "A cooperative interaction between U2AF65 and mBBP/SF1 facilitates branchpoint region recognition". Genes & Development. 12 (6): 858–867. doi:10.1101/gad.12.6.858. PMC 316625. PMID 9512519.
- Rudner DZ, Kanaar R, Breger KS, Rio DC (April 1998). "Interaction between subunits of heterodimeric splicing factor U2AF is essential in vivo". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (4): 1765–1773. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.4.1765. PMC 121406. PMID 9528748.
- Lallena MJ, Martínez C, Valcárcel J, Correas I (July 1998). "Functional association of nuclear protein 4.1 with pre-mRNA splicing factors". Journal of Cell Science. 111 (14): 1963–1971. doi:10.1242/jcs.111.14.1963. PMID 9645944.
- Gozani O, Potashkin J, Reed R (August 1998). "A potential role for U2AF-SAP 155 interactions in recruiting U2 snRNP to the branch site". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (8): 4752–4760. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.8.4752. PMC 109061. PMID 9671485.
- Neubauer G, King A, Rappsilber J, Calvio C, Watson M, Ajuh P, et al. (September 1998). "Mass spectrometry and EST-database searching allows characterization of the multi-protein spliceosome complex". Nature Genetics. 20 (1): 46–50. doi:10.1038/1700. PMID 9731529. S2CID 585778.
- Davies RC, Calvio C, Bratt E, Larsson SH, Lamond AI, Hastie ND (October 1998). "WT1 interacts with the splicing factor U2AF65 in an isoform-dependent manner and can be incorporated into spliceosomes". Genes & Development. 12 (20): 3217–3225. doi:10.1101/gad.12.20.3217. PMC 317218. PMID 9784496.
- Ito T, Muto Y, Green MR, Yokoyama S (August 1999). "Solution structures of the first and second RNA-binding domains of human U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle auxiliary factor (U2AF(65))". The EMBO Journal. 18 (16): 4523–4534. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.16.4523. PMC 1171527. PMID 10449418.
- Wang X, Bruderer S, Rafi Z, Xue J, Milburn PJ, Krämer A, Robinson PJ (August 1999). "Phosphorylation of splicing factor SF1 on Ser20 by cGMP-dependent protein kinase regulates spliceosome assembly". The EMBO Journal. 18 (16): 4549–4559. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.16.4549. PMC 1171529. PMID 10449420.
- Ladomery MR, Slight J, Mc Ghee S, Hastie ND (December 1999). "Presence of WT1, the Wilm's tumor suppressor gene product, in nuclear poly(A)(+) ribonucleoprotein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (51): 36520–36526. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.51.36520. PMID 10593950.
- v
- t
- e
-
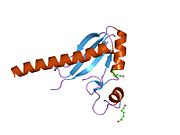 1jmt: X-ray Structure of a Core U2AF65/U2AF35 Heterodimer
1jmt: X-ray Structure of a Core U2AF65/U2AF35 Heterodimer -
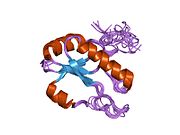 1o0p: Solution Structure of the third RNA Recognition Motif (RRM) of U2AF65 in complex with an N-terminal SF1 peptide
1o0p: Solution Structure of the third RNA Recognition Motif (RRM) of U2AF65 in complex with an N-terminal SF1 peptide -
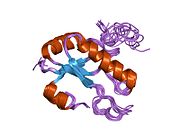 1opi: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE THIRD RNA RECOGNITION MOTIF (RRM) OF U2AF65 IN COMPLEX WITH AN N-TERMINAL SF1 PEPTIDE
1opi: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE THIRD RNA RECOGNITION MOTIF (RRM) OF U2AF65 IN COMPLEX WITH AN N-TERMINAL SF1 PEPTIDE -
 1u2f: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE FIRST RNA-BINDING DOMAIN OF HU2AF65
1u2f: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE FIRST RNA-BINDING DOMAIN OF HU2AF65 -
 2hzc: Crystal structure of the N-terminal RRM of the U2AF large subunit
2hzc: Crystal structure of the N-terminal RRM of the U2AF large subunit -
 2u2f: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE SECOND RNA-BINDING DOMAIN OF HU2AF65
2u2f: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE SECOND RNA-BINDING DOMAIN OF HU2AF65