Ureidopenicillin
Group of chemical compounds
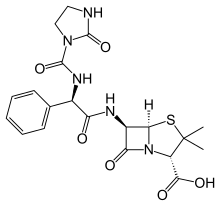


The ureidopenicillins are a group of penicillins which are active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[citation needed]
There are three ureidopenicillins in clinical use:[1]
- Azlocillin
- Piperacillin
- Mezlocillin
They are mostly ampicillin derivatives in which the amino acid side chain has been converted to a variety of cyclic ureas. It is speculated that the added side chain mimics a longer segment of the peptidoglycan chain, more than ampicillin, and thus would bind more easily to the penicillin-binding proteins. Ureidopenicillins are not resistant to beta-lactamases.[citation needed]
They are used parenterally, and are particularly indicated in infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria.[citation needed]
References
- ^ "Mayo Clinic Proceedings". Archived from the original on 2020-05-26. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- v
- t
- e










