Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| KCNMB2, ball and chain domain |
|---|
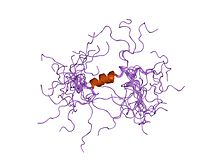 solution structure of the cytoplasmic n-terminus of the bk beta-subunit kcnmb2 |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Symbol | KcnmB2_inactiv |
|---|
| Pfam | PF09303 |
|---|
| InterPro | IPR015382 |
|---|
| Available protein structures: |
|---|
| Pfam | structures / ECOD |
|---|
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
|---|
| PDBsum | structure summary |
|---|
|
Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNMB2 gene.[5][6]
Big Potassium (BK) channels are large conductance, voltage and calcium-sensitive potassium channels which are fundamental to the control of smooth muscle tone and neuronal excitability. BK channels can contain two distinct subunits: a pore-forming alpha subunit and a modulatory beta subunit. Each complete BK channel contains four copies of the pore-forming alpha subunit and up to four beta subunits. The protein encoded by the KCNMB2 gene is an auxiliary beta subunit which influences the calcium sensitivity of BK currents and, following activation of BK current, causes persistent inactivation. The subunit encoded by the KCNMB2 gene is expressed in various endocrine cells, including pancreas and adrenal chromaffin cells. It is also found in the brain, including the hippocampus. The KCNMB2 gene is homologous to three other genes found in mammalian genomes: KCNMB1 (found primarily in smooth muscle), KCNMB3, and KCNMB4 (the primary brain BK auxiliary subunit).[6]
Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-2 comprises two domains. An N-terminal cytoplasmic domain, the ball and chain domain, which is responsible for the fast inactivation of these channels,[7] and a C-terminal calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunit domain. The N-terminal domain only occurs in calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-2, while the C-terminal domain is found in related proteins.
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000197584 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000037610 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Wallner M, Meera P, Toro L (May 1999). "Molecular basis of fast inactivation in voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channels: a transmembrane beta-subunit homolog". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 96 (7): 4137–42. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.4137W. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.7.4137. PMC 22433. PMID 10097176.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: KCNMB2 potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, beta member 2".
- ^ Bentrop D, Beyermann M, Wissmann R, Fakler B (November 2001). "NMR structure of the "ball-and-chain" domain of KCNMB2, the beta 2-subunit of large conductance Ca2+- and voltage-activated potassium channels". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (45): 42116–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107118200. PMID 11517232.
Further reading
- Orio P, Rojas P, Ferreira G, Latorre R (2002). "New disguises for an old channel: MaxiK channel beta-subunits". News Physiol. Sci. 17 (4): 156–61. doi:10.1152/nips.01387.2002. hdl:10533/173696. PMID 12136044.
- Xia XM, Ding JP, Lingle CJ (1999). "Molecular basis for the inactivation of Ca2+- and voltage-dependent BK channels in adrenal chromaffin cells and rat insulinoma tumor cells". J. Neurosci. 19 (13): 5255–64. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-13-05255.1999. PMC 6782330. PMID 10377337.
- Brenner R, Jegla TJ, Wickenden A, et al. (2000). "Cloning and functional characterization of novel large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunits, hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (9): 6453–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.9.6453. PMID 10692449.
- Liu QH, Williams DA, McManus C, et al. (2000). "HIV-1 gp120 and chemokines activate ion channels in primary macrophages through CCR5 and CXCR4 stimulation". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (9): 4832–7. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.4832L. doi:10.1073/pnas.090521697. PMC 18318. PMID 10758170.
- Uebele VN, Lagrutta A, Wade T, et al. (2000). "Cloning and functional expression of two families of beta-subunits of the large conductance calcium-activated K+ channel". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (30): 23211–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M910187199. PMID 10766764.
- Meera P, Wallner M, Toro L (2000). "A neuronal beta subunit (KCNMB4) makes the large conductance, voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channel resistant to charybdotoxin and iberiotoxin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (10): 5562–7. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.5562M. doi:10.1073/pnas.100118597. PMC 25868. PMID 10792058.
- Bentrop D, Beyermann M, Wissmann R, Fakler B (2001). "NMR structure of the "ball-and-chain" domain of KCNMB2, the beta 2-subunit of large conductance Ca2+- and voltage-activated potassium channels". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (45): 42116–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107118200. PMID 11517232.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Xia XM, Ding JP, Lingle CJ (2003). "Inactivation of BK channels by the NH2 terminus of the beta2 auxiliary subunit: an essential role of a terminal peptide segment of three hydrophobic residues". J. Gen. Physiol. 121 (2): 125–48. doi:10.1085/jgp.20028667. PMC 2217327. PMID 12566540.
- Hartness ME, Brazier SP, Peers C, et al. (2004). "Post-transcriptional control of human maxiK potassium channel activity and acute oxygen sensitivity by chronic hypoxia". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (51): 51422–32. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309463200. PMID 14522958.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Orio P, Torres Y, Rojas P, et al. (2006). "Structural determinants for functional coupling between the beta and alpha subunits in the Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channel". J. Gen. Physiol. 127 (2): 191–204. doi:10.1085/jgp.200509370. PMC 2151488. PMID 16446507.
- Zeng XH, Benzinger GR, Xia XM, Lingle CJ (2007). "BK channels with beta3a subunits generate use-dependent slow afterhyperpolarizing currents by an inactivation-coupled mechanism". J. Neurosci. 27 (17): 4707–15. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0758-07.2007. PMC 6672991. PMID 17460083.
- Zarei MM, Song M, Wilson RJ, et al. (2007). "Endocytic trafficking signals in KCNMB2 regulate surface expression of a large conductance voltage and Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel". Neuroscience. 147 (1): 80–9. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.04.019. PMID 17521822. S2CID 24449192.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from the public domain
Pfam and
InterPro: IPR015382
 | This membrane protein–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |


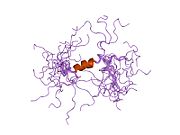 1jo6: Solution structure of the cytoplasmic N-terminus of the BK beta-subunit KCNMB2
1jo6: Solution structure of the cytoplasmic N-terminus of the BK beta-subunit KCNMB2