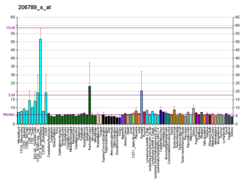
POU2F1
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| POU2F1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | POU2F1, OCT1, OTF1, oct-1B, POU class 2 homeobox 1, Oct1Z | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 164175; MGI: 101898; HomoloGene: 37658; GeneCards: POU2F1; OMA:POU2F1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU2F1 gene.[5][6]
Interactions
POU2F1 has been shown to interact with:
- EPRS,[7]
- Glucocorticoid receptor,[8][9][10]
- Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase,[11]
- Host cell factor C1,[12][13]
- Ku80,[14][15]
- MNAT1[16]
- NPAT,[11]
- Nuclear receptor co-repressor 2,[17]
- POU2AF1,[18][19][20]
- RELA,[21]
- Retinoid X receptor alpha,[8][22]
- SNAPC4,[18][23]
- Sp1 transcription factor,[24][25] and
- TATA binding protein.[26]
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000143190 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026565 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Roberts SB, Segil N, Heintz N (October 1991). "Differential phosphorylation of the transcription factor Oct1 during the cell cycle". Science. 253 (5023): 1022–6. doi:10.1126/science.1887216. PMID 1887216. S2CID 23291453.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: POU2F1 POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 1".
- ^ Nie J, Sakamoto S, Song D, Qu Z, Ota K, Taniguchi T (March 1998). "Interaction of Oct-1 and automodification domain of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase". FEBS Lett. 424 (1–2): 27–32. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00131-8. PMID 9537509. S2CID 872132.
- ^ a b Préfontaine GG, Walther R, Giffin W, Lemieux ME, Pope L, Haché RJ (September 1999). "Selective binding of steroid hormone receptors to octamer transcription factors determines transcriptional synergism at the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (38): 26713–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.38.26713. PMID 10480874.
- ^ Wang JM, Préfontaine GG, Lemieux ME, Pope L, Akimenko MA, Haché RJ (October 1999). "Developmental effects of ectopic expression of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain are alleviated by an amino acid substitution that interferes with homeodomain binding". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (10): 7106–22. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.10.7106. PMC 84705. PMID 10490647.
- ^ Préfontaine GG, Lemieux ME, Giffin W, Schild-Poulter C, Pope L, LaCasse E, Walker P, Haché RJ (June 1998). "Recruitment of octamer transcription factors to DNA by glucocorticoid receptor". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (6): 3416–30. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.6.3416. PMC 108923. PMID 9584182.
- ^ a b McKnight S (July 2003). "Gene switching by metabolic enzymes--how did you get on the invitation list?". Cell. 114 (2): 150–2. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00563-4. PMID 12887915. S2CID 895360.
- ^ La Boissière S, Hughes T, O'Hare P (January 1999). "HCF-dependent nuclear import of VP16". EMBO J. 18 (2): 480–9. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.2.480. PMC 1171141. PMID 9889203.
- ^ Kristie TM, Sharp PA (March 1993). "Purification of the cellular C1 factor required for the stable recognition of the Oct-1 homeodomain by the herpes simplex virus alpha-trans-induction factor (VP16)". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (9): 6525–34. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53282-8. PMID 8454622.
- ^ Schild-Poulter C, Pope L, Giffin W, Kochan JC, Ngsee JK, Traykova-Andonova M, Haché RJ (May 2001). "The binding of Ku antigen to homeodomain proteins promotes their phosphorylation by DNA-dependent protein kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (20): 16848–56. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100768200. PMID 11279128.
- ^ Matheos D, Ruiz MT, Price GB, Zannis-Hadjopoulos M (October 2002). "Ku antigen, an origin-specific binding protein that associates with replication proteins, is required for mammalian DNA replication". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1578 (1–3): 59–72. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(02)00497-9. PMID 12393188.
- ^ Inamoto S, Segil N, Pan ZQ, Kimura M, Roeder RG (November 1997). "The cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase (CAK) assembly factor, MAT1, targets and enhances CAK activity on the POU domains of octamer transcription factors". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (47): 29852–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.47.29852. PMID 9368058.
- ^ Kakizawa T, Miyamoto T, Ichikawa K, Takeda T, Suzuki S, Mori J, Kumagai M, Yamashita K, Hashizume K (March 2001). "Silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors interacts with octamer transcription factor-1 and acts as a transcriptional repressor". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (13): 9720–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008531200. PMID 11134019.
- ^ a b Wong MW, Henry RW, Ma B, Kobayashi R, Klages N, Matthias P, Strubin M, Hernandez N (January 1998). "The large subunit of basal transcription factor SNAPc is a Myb domain protein that interacts with Oct-1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (1): 368–77. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.1.368. PMC 121507. PMID 9418884.
- ^ Chasman D, Cepek K, Sharp PA, Pabo CO (October 1999). "Crystal structure of an OCA-B peptide bound to an Oct-1 POU domain/octamer DNA complex: specific recognition of a protein-DNA interface". Genes Dev. 13 (20): 2650–7. doi:10.1101/gad.13.20.2650. PMC 317104. PMID 10541551.
- ^ Lee L, Stollar E, Chang J, Grossmann JG, O'Brien R, Ladbury J, Carpenter B, Roberts S, Luisi B (June 2001). "Expression of the Oct-1 transcription factor and characterization of its interactions with the Bob1 coactivator". Biochemistry. 40 (22): 6580–8. doi:10.1021/bi010095x. PMID 11380252.
- ^ van Heel DA, Udalova IA, De Silva AP, McGovern DP, Kinouchi Y, Hull J, Lench NJ, Cardon LR, Carey AH, Jewell DP, Kwiatkowski D (May 2002). "Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with a TNF polymorphism that affects an interaction between the OCT1 and NF(-kappa)B transcription factors". Hum. Mol. Genet. 11 (11): 1281–9. doi:10.1093/hmg/11.11.1281. PMID 12019209.
- ^ Kakizawa T, Miyamoto T, Ichikawa K, Kaneko A, Suzuki S, Hara M, Nagasawa T, Takeda T, Mori Ji, Kumagai M, Hashizume K (July 1999). "Functional interaction between Oct-1 and retinoid X receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (27): 19103–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.27.19103. PMID 10383413.
- ^ Hovde S, Brooks A, Strong K, Geiger JH (March 2002). "Crystallization of the Oct-1/SNAP190 peptide/DNA complex". Acta Crystallogr. D. 58 (Pt 3): 511–2. doi:10.1107/s0907444901021461. PMID 11856838.
- ^ Ström AC, Forsberg M, Lillhager P, Westin G (June 1996). "The transcription factors Sp1 and Oct-1 interact physically to regulate human U2 snRNA gene expression". Nucleic Acids Res. 24 (11): 1981–6. doi:10.1093/nar/24.11.1981. PMC 145891. PMID 8668525.
- ^ Gunther M, Laithier M, Brison O (July 2000). "A set of proteins interacting with transcription factor Sp1 identified in a two-hybrid screening". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 210 (1–2): 131–42. doi:10.1023/A:1007177623283. PMID 10976766. S2CID 1339642.
- ^ Zwilling S, Annweiler A, Wirth T (May 1994). "The POU domains of the Oct1 and Oct2 transcription factors mediate specific interaction with TBP". Nucleic Acids Res. 22 (9): 1655–62. doi:10.1093/nar/22.9.1655. PMC 308045. PMID 8202368.
Further reading
- Hsieh CL, Sturm R, Herr W, Francke U (1990). "The gene for the ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct–1 is on human chromosome 1, region cen-q32, and near Ly-22 and Ltw-4 on mouse chromosome 1". Genomics. 6 (4): 666–72. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90502-L. PMID 2341156.
- Sturm RA, Das G, Herr W (1989). "The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct–1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain". Genes Dev. 2 (12A): 1582–99. doi:10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. PMID 2905684.
- Nakshatri H, Nakshatri P, Currie RA (1995). "Interaction of Oct–1 with TFIIB. Implications for a novel response elicited through the proximal octamer site of the lipoprotein lipase promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (33): 19613–23. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.33.19613. hdl:1805/18867. PMID 7642649.
- Cox M, van Tilborg PJ, de Laat W, Boelens R, van Leeuwen HC, van der Vliet PC, Kaptein R (1995). "Solution structure of the Oct–1 POU homeodomain determined by NMR and restrained molecular dynamics". J. Biomol. NMR. 6 (1): 23–32. doi:10.1007/BF00417488. PMID 7663141. S2CID 26063646.
- Jeang KT, Chun R, Lin NH, Gatignol A, Glabe CG, Fan H (1993). "In vitro and in vivo binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein and Sp1 transcription factor". J. Virol. 67 (10): 6224–33. doi:10.1128/JVI.67.10.6224-6233.1993. PMC 238044. PMID 7690421.
- Zwilling S, König H, Wirth T (1995). "High mobility group protein 2 functionally interacts with the POU domains of octamer transcription factors". EMBO J. 14 (6): 1198–208. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07103.x. PMC 398197. PMID 7720710.
- Sturm RA, Eyre HJ, Baker E, Sutherland GR (1995). "The human OTF1 locus which overlaps the CD3Z gene is located at 1q22→q23". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 68 (3–4): 231–2. doi:10.1159/000133919. PMID 7842742.
- Klemm JD, Rould MA, Aurora R, Herr W, Pabo CO (1994). "Crystal structure of the Oct–1 POU domain bound to an octamer site: DNA recognition with tethered DNA-binding modules". Cell. 77 (1): 21–32. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90231-3. PMID 8156594. S2CID 36371069.
- Zwilling S, Annweiler A, Wirth T (1994). "The POU domains of the Oct1 and Oct2 transcription factors mediate specific interaction with TBP". Nucleic Acids Res. 22 (9): 1655–62. doi:10.1093/nar/22.9.1655. PMC 308045. PMID 8202368.
- Kristie TM, Sharp PA (1993). "Purification of the cellular C1 factor required for the stable recognition of the Oct–1 homeodomain by the herpes simplex virus alpha-trans-induction factor (VP16)". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (9): 6525–34. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53282-8. PMID 8454622.
- Assa-Munt N, Mortishire-Smith RJ, Aurora R, Herr W, Wright PE (1993). "The solution structure of the Oct–1 POU-specific domain reveals a striking similarity to the bacteriophage lambda repressor DNA-binding domain". Cell. 73 (1): 193–205. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90171-L. PMID 8462099. S2CID 24276357.
- Dekker N, Cox M, Boelens R, Verrijzer CP, van der Vliet PC, Kaptein R (1993). "Solution structure of the POU-specific DNA-binding domain of Oct–1". Nature. 362 (6423): 852–5. Bibcode:1993Natur.362..852D. doi:10.1038/362852a0. PMID 8479524. S2CID 21540451.
- Ström AC, Forsberg M, Lillhager P, Westin G (1996). "The transcription factors Sp1 and Oct–1 interact physically to regulate human U2 snRNA gene expression". Nucleic Acids Res. 24 (11): 1981–6. doi:10.1093/nar/24.11.1981. PMC 145891. PMID 8668525.
- Inamoto S, Segil N, Pan ZQ, Kimura M, Roeder RG (1997). "The cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase (CAK) assembly factor, MAT1, targets and enhances CAK activity on the POU domains of octamer transcription factors". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (47): 29852–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.47.29852. PMID 9368058.
- Wong MW, Henry RW, Ma B, Kobayashi R, Klages N, Matthias P, Strubin M, Hernandez N (1998). "The Large Subunit of Basal Transcription Factor SNAPc Is a Myb Domain Protein That Interacts with Oct–1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (1): 368–77. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.1.368. PMC 121507. PMID 9418884.
- Nie J, Sakamoto S, Song D, Qu Z, Ota K, Taniguchi T (1998). "Interaction of Oct–1 and automodification domain of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase". FEBS Lett. 424 (1–2): 27–32. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00131-8. PMID 9537509. S2CID 872132.
- Préfontaine GG, Lemieux ME, Giffin W, Schild-Poulter C, Pope L, LaCasse E, Walker P, Haché RJ (1998). "Recruitment of Octamer Transcription Factors to DNA by Glucocorticoid Receptor". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (6): 3416–30. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.6.3416. PMC 108923. PMID 9584182.
- La Boissière S, Hughes T, O'Hare P (1999). "HCF-dependent nuclear import of VP16". EMBO J. 18 (2): 480–9. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.2.480. PMC 1171141. PMID 9889203.
External links
- POU2F1+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- v
- t
- e
PDB gallery
-
 1cqt: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A TERNARY COMPLEX CONTAINING AN OCA-B PEPTIDE, THE OCT-1 POU DOMAIN, AND AN OCTAMER ELEMENT
1cqt: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A TERNARY COMPLEX CONTAINING AN OCA-B PEPTIDE, THE OCT-1 POU DOMAIN, AND AN OCTAMER ELEMENT -
 1e3o: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF OCT-1 POU DIMER BOUND TO MORE
1e3o: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF OCT-1 POU DIMER BOUND TO MORE -
 1gt0: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A POU/HMG/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX
1gt0: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A POU/HMG/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX -
 1hf0: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE DNA-BINDING DOMAIN OF OCT-1 BOUND TO DNA AS A DIMER
1hf0: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE DNA-BINDING DOMAIN OF OCT-1 BOUND TO DNA AS A DIMER -
 1o4x: TERNARY COMPLEX OF THE DNA BINDING DOMAINS OF THE OCT1 AND SOX2 TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS WITH A 19MER OLIGONUCLEOTIDE FROM THE HOXB1 REGULATORY ELEMENT
1o4x: TERNARY COMPLEX OF THE DNA BINDING DOMAINS OF THE OCT1 AND SOX2 TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS WITH A 19MER OLIGONUCLEOTIDE FROM THE HOXB1 REGULATORY ELEMENT -
 1oct: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE OCT-1 POU DOMAIN BOUND TO AN OCTAMER SITE: DNA RECOGNITION WITH TETHERED DNA-BINDING MODULES
1oct: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE OCT-1 POU DOMAIN BOUND TO AN OCTAMER SITE: DNA RECOGNITION WITH TETHERED DNA-BINDING MODULES -
 1pog: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE OCT-1 POU-HOMEO DOMAIN DETERMINED BY NMR AND RESTRAINED MOLECULAR DYNAMICS
1pog: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE OCT-1 POU-HOMEO DOMAIN DETERMINED BY NMR AND RESTRAINED MOLECULAR DYNAMICS -
 1pou: THE SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE OCT-1 POU-SPECIFIC DOMAIN REVEALS A STRIKING SIMILARITY TO THE BACTERIOPHAGE LAMBDA REPRESSOR DNA-BINDING DOMAIN
1pou: THE SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE OCT-1 POU-SPECIFIC DOMAIN REVEALS A STRIKING SIMILARITY TO THE BACTERIOPHAGE LAMBDA REPRESSOR DNA-BINDING DOMAIN