Transcriptional repressor protein
| YY1 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1UBD, 1ZNM, 4C5I |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | YY1, DELTA, INO80S, NF-E1, UCRBP, YIN-YANG-1, YY1 transcription factor, GADEVS |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600013; MGI: 99150; HomoloGene: 2556; GeneCards: YY1; OMA:YY1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 14 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 14q32.2 | Start | 100,238,298 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 100,282,788 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 12 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 12 F1|12 59.58 cM | Start | 108,758,899 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 108,786,074 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - ganglionic eminence
- endothelial cell
- middle temporal gyrus
- Brodmann area 23
- rectum
- monocyte
- thymus
- sural nerve
- islet of Langerhans
- stromal cell of endometrium
|
| | Top expressed in | - medullary collecting duct
- primitive streak
- ureter
- renal corpuscle
- abdominal wall
- left lung lobe
- cumulus cell
- endocardial cushion
- atrioventricular valve
- urothelium
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - DNA binding
- transcription corepressor activity
- transcription coactivator activity
- zinc ion binding
- metal ion binding
- protein binding
- four-way junction DNA binding
- cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- RNA binding
- nucleic acid binding
- SMAD binding
- RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- histone deacetylase binding
| | Cellular component | - Ino80 complex
- nuclear matrix
- nucleus
- nucleoplasm
- transcription regulator complex
- cytoplasm
- PcG protein complex
| | Biological process | - cell differentiation
- DNA recombination
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- cellular response to UV
- negative regulation of gene expression
- transcription, DNA-templated
- cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
- double-strand break repair via homologous recombination
- spermatogenesis
- DNA repair
- protein deubiquitination
- negative regulation of interferon-beta production
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- RNA localization
- anterior/posterior pattern specification
- response to UV-C
- positive regulation of gene expression
- response to prostaglandin F
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- camera-type eye morphogenesis
- chromosome organization
- cellular response to interleukin-1
- negative regulation of pri-miRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II
- negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 14: 100.24 – 100.28 Mb | Chr 12: 108.76 – 108.79 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
YY1 (Yin Yang 1)[5] is a transcriptional repressor protein in humans that is encoded by the YY1 gene.[6][7]
Function
YY1 is a ubiquitously distributed transcription factor belonging to the GLI-Kruppel class of zinc finger proteins. The protein is involved in repressing and activating a diverse number of promoters. Hence, the YY in the name stands for "yin-yang." YY1 may direct histone deacetylases and histone acetyltransferases to a promoter in order to activate or repress the promoter, thus implicating histone modification in the function of YY1.[8] YY1 promotes enhancer-promoter chromatin loops by forming dimers and promoting DNA interactions. Its dysregulation disrupts enhancer-promoter loops and gene expression.[9][10]
Clinical significance
YY1 heterozygous deletions, missense, and nonsense mutations cause Gabriele-DeVries syndrome (GADEVS),[11][12] an autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by intellectual disability, dysmorphic facial features, feeding problems, intrauterine growth restriction, variable cognitive impairment, behavioral problems and other congenital malformations.[10] A website is available in order to collect and share clinical information between clinicians and the families of affected individuals.[13]
Interactions
YY1 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000100811 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021264 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Thiaville MM, Kim J (2011). "Oncogenic potential of yin yang 1 mediated through control of imprinted genes". Critical Reviews in Oncogenesis. 16 (3–4): 199–209. doi:10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i3-4.40. PMC 3392609. PMID 22248054.
- ^ Shi Y, Seto E, Chang LS, Shenk T (October 1991). "Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein". Cell. 67 (2): 377–88. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. PMID 1655281. S2CID 19399858.
- ^ Zhu W, Lossie AC, Camper SA, Gumucio DL (April 1994). "Chromosomal localization of the transcription factor YY1 in the mouse and human". Mammalian Genome. 5 (4): 234–6. doi:10.1007/BF00360552. hdl:2027.42/47010. PMID 7912122. S2CID 27296553.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: YY1 YY1 transcription factor".
- ^ Weintraub AS, Li CH, Zamudio AV, Sigova AA, Hannett NM, Day DS, et al. (December 2017). "YY1 Is a Structural Regulator of Enhancer-Promoter Loops". Cell. 171 (7): 1573–1588.e28. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.008. PMC 5785279. PMID 29224777.
- ^ a b Gabriele M, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Germain PL, Vitriolo A, Kumar R, Douglas E, et al. (June 2017). "YY1 Haploinsufficiency Causes an Intellectual Disability Syndrome Featuring Transcriptional and Chromatin Dysfunction". American Journal of Human Genetics. 100 (6): 907–925. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.05.006. PMC 5473733. PMID 28575647.
- ^ "OMIM:GABRIELE-DE VRIES SYNDROME".
- ^ Nabais Sá, M. J.; Gabriele, M.; Testa, G.; de Vries BBA; Adam, M. P.; Ardinger, H. H.; Pagon, R. A.; Wallace, S. E.; Bean LJH; Stephens, K.; Amemiya, A. (1993). "Gabriele-de Vries Syndrome". PMID 31145572.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires |journal= (help) - ^ "YY1 – Collect information about clinic management and research projects". YY1.
- ^ Li M, Baumeister P, Roy B, Phan T, Foti D, Luo S, Lee AS (July 2000). "ATF6 as a transcription activator of the endoplasmic reticulum stress element: thapsigargin stress-induced changes and synergistic interactions with NF-Y and YY1". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 20 (14): 5096–106. doi:10.1128/mcb.20.14.5096-5106.2000. PMC 85959. PMID 10866666.
- ^ a b c Yao YL, Yang WM, Seto E (September 2001). "Regulation of transcription factor YY1 by acetylation and deacetylation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 21 (17): 5979–91. doi:10.1128/mcb.21.17.5979-5991.2001. PMC 87316. PMID 11486036.
- ^ Lee JS, Galvin KM, See RH, Eckner R, Livingston D, Moran E, Shi Y (May 1995). "Relief of YY1 transcriptional repression by adenovirus E1A is mediated by E1A-associated protein p300". Genes & Development. 9 (10): 1188–98. doi:10.1101/gad.9.10.1188. PMID 7758944.
- ^ Yang WM, Yao YL, Seto E (September 2001). "The FK506-binding protein 25 functionally associates with histone deacetylases and with transcription factor YY1". The EMBO Journal. 20 (17): 4814–25. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.17.4814. PMC 125595. PMID 11532945.
- ^ a b Yang WM, Yao YL, Sun JM, Davie JR, Seto E (October 1997). "Isolation and characterization of cDNAs corresponding to an additional member of the human histone deacetylase gene family". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (44): 28001–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.44.28001. PMID 9346952.
- ^ Kalenik JL, Chen D, Bradley ME, Chen SJ, Lee TC (February 1997). "Yeast two-hybrid cloning of a novel zinc finger protein that interacts with the multifunctional transcription factor YY1". Nucleic Acids Research. 25 (4): 843–9. doi:10.1093/nar/25.4.843. PMC 146511. PMID 9016636.
- ^ Shrivastava A, Saleque S, Kalpana GV, Artandi S, Goff SP, Calame K (December 1993). "Inhibition of transcriptional regulator Yin-Yang-1 by association with c-Myc". Science. 262 (5141): 1889–92. Bibcode:1993Sci...262.1889S. doi:10.1126/science.8266081. PMID 8266081.
- ^ Yeh TS, Lin YM, Hsieh RH, Tseng MJ (October 2003). "Association of transcription factor YY1 with the high molecular weight Notch complex suppresses the transactivation activity of Notch". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (43): 41963–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304353200. PMID 12913000.
- ^ García E, Marcos-Gutiérrez C, del Mar Lorente M, Moreno JC, Vidal M (June 1999). "RYBP, a new repressor protein that interacts with components of the mammalian Polycomb complex, and with the transcription factor YY1". The EMBO Journal. 18 (12): 3404–18. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.12.3404. PMC 1171420. PMID 10369680.
- ^ Huang NE, Lin CH, Lin YS, Yu WC (June 2003). "Modulation of YY1 activity by SAP30". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 306 (1): 267–75. doi:10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00966-5. PMID 12788099.
- ^ Fu CY, Wang P, Tsai HJ (November 2017). "Competitive binding between Seryl-tRNA synthetase/YY1 complex and NFKB1 at the distal segment results in differential regulation of human vegfa promoter activity during angiogenesis". Nucleic Acids Research. 45 (5): 2423–2437. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1187. PMC 5389716. PMID 27913726.
Further reading
- Thomas MJ, Seto E (August 1999). "Unlocking the mechanisms of transcription factor YY1: are chromatin modifying enzymes the key?". Gene. 236 (2): 197–208. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00261-9. PMID 10452940.
- Park K, Atchison ML (November 1991). "Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 88 (21): 9804–8. Bibcode:1991PNAS...88.9804P. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804. PMC 52809. PMID 1946405.
- Yang WM, Inouye CJ, Seto E (June 1995). "Cyclophilin A and FKBP12 interact with YY1 and alter its transcriptional activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (25): 15187–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.25.15187. PMID 7541038.
- Lee JS, Galvin KM, See RH, Eckner R, Livingston D, Moran E, Shi Y (May 1995). "Relief of YY1 transcriptional repression by adenovirus E1A is mediated by E1A-associated protein p300". Genes & Development. 9 (10): 1188–98. doi:10.1101/gad.9.10.1188. PMID 7758944.
- Zhou Q, Gedrich RW, Engel DA (July 1995). "Transcriptional repression of the c-fos gene by YY1 is mediated by a direct interaction with ATF/CREB". Journal of Virology. 69 (7): 4323–30. doi:10.1128/JVI.69.7.4323-4330.1995. PMC 189172. PMID 7769693.
- Shrivastava A, Saleque S, Kalpana GV, Artandi S, Goff SP, Calame K (December 1993). "Inhibition of transcriptional regulator Yin-Yang-1 by association with c-Myc". Science. 262 (5141): 1889–92. Bibcode:1993Sci...262.1889S. doi:10.1126/science.8266081. PMID 8266081.
- Becker KG, Swergold GD, Ozato K, Thayer RE (October 1993). "Binding of the ubiquitous nuclear transcription factor YY1 to a cis regulatory sequence in the human LINE-1 transposable element". Human Molecular Genetics. 2 (10): 1697–702. doi:10.1093/hmg/2.10.1697. PMID 8268924.
- Margolis DM, Somasundaran M, Green MR (February 1994). "Human transcription factor YY1 represses human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcription and virion production". Journal of Virology. 68 (2): 905–10. doi:10.1128/JVI.68.2.905-910.1994. PMC 236527. PMID 8289393.
- Lee JS, Galvin KM, Shi Y (July 1993). "Evidence for physical interaction between the zinc-finger transcription factors YY1 and Sp1". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (13): 6145–9. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.6145L. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.13.6145. PMC 46884. PMID 8327494.
- Houbaviy HB, Usheva A, Shenk T, Burley SK (November 1996). "Cocrystal structure of YY1 bound to the adeno-associated virus P5 initiator". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 93 (24): 13577–82. Bibcode:1996PNAS...9313577H. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.24.13577. PMC 19349. PMID 8942976.
- Kalenik JL, Chen D, Bradley ME, Chen SJ, Lee TC (February 1997). "Yeast two-hybrid cloning of a novel zinc finger protein that interacts with the multifunctional transcription factor YY1". Nucleic Acids Research. 25 (4): 843–9. doi:10.1093/nar/25.4.843. PMC 146511. PMID 9016636.
- Cole EG, Gaston K (September 1997). "A functional YY1 binding site is necessary and sufficient to activate Surf-1 promoter activity in response to serum growth factors". Nucleic Acids Research. 25 (18): 3705–11. doi:10.1093/nar/25.18.3705. PMC 146936. PMID 9278494.
- Yang WM, Yao YL, Sun JM, Davie JR, Seto E (October 1997). "Isolation and characterization of cDNAs corresponding to an additional member of the human histone deacetylase gene family". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (44): 28001–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.44.28001. PMID 9346952.
- Romerio F, Gabriel MN, Margolis DM (December 1997). "Repression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through the novel cooperation of human factors YY1 and LSF". Journal of Virology. 71 (12): 9375–82. doi:10.1128/JVI.71.12.9375-9382.1997. PMC 230241. PMID 9371597.
- McNeil S, Guo B, Stein JL, Lian JB, Bushmeyer S, Seto E, Atchison ML, Penman S, van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS (March 1998). "Targeting of the YY1 transcription factor to the nucleolus and the nuclear matrix in situ: the C-terminus is a principal determinant for nuclear trafficking". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 68 (4): 500–10. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19980315)68:4<500::AID-JCB9>3.0.CO;2-U. PMID 9493912. S2CID 34077497.
- Viles JH, Patel SU, Mitchell JB, Moody CM, Justice DE, Uppenbrink J, Doyle PM, Harris CJ, Sadler PJ, Thornton JM (June 1998). "Design, synthesis and structure of a zinc finger with an artificial beta-turn". Journal of Molecular Biology. 279 (4): 973–86. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.1764. PMID 9642075.
- Yao YL, Dupont BR, Ghosh S, Fang Y, Leach RJ, Seto E (August 1998). "Cloning, chromosomal localization and promoter analysis of the human transcription factor YY1". Nucleic Acids Research. 26 (16): 3776–83. doi:10.1093/nar/26.16.3776. PMC 147783. PMID 9685495.
U== External links ==
- FactorBook YY1
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P25490 (Transcriptional repressor protein YY1) at the PDBe-KB.
|
|---|
(1) Basic domains |
|---|
| (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) | |
|---|
| (1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) | | Group A | |
|---|
| Group B | |
|---|
Group C
bHLH-PAS | |
|---|
| Group D | |
|---|
| Group E | |
|---|
Group F
bHLH-COE | |
|---|
|
|---|
| (1.3) bHLH-ZIP | |
|---|
| (1.4) NF-1 | |
|---|
| (1.5) RF-X | |
|---|
| (1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH) | |
|---|
|
|
(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains |
|---|
| (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4) | | subfamily 1 | |
|---|
| subfamily 2 | |
|---|
| subfamily 3 | |
|---|
| subfamily 4 | |
|---|
| subfamily 5 | |
|---|
| subfamily 6 | |
|---|
| subfamily 0 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| (2.2) Other Cys4 | |
|---|
| (2.3) Cys2His2 | |
|---|
| (2.4) Cys6 | |
|---|
| (2.5) Alternating composition | |
|---|
| (2.6) WRKY | |
|---|
|
|
|
(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts |
|---|
|
|
(0) Other transcription factors |
|---|
|
|
see also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies |

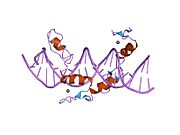 1ubd: CO-CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN YY1 ZINC FINGER DOMAIN BOUND TO THE ADENO-ASSOCIATED VIRUS P5 INITIATOR ELEMENT
1ubd: CO-CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN YY1 ZINC FINGER DOMAIN BOUND TO THE ADENO-ASSOCIATED VIRUS P5 INITIATOR ELEMENT


















