| TFAP4 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | TFAP4, AP-4, bHLHc41, transcription factor AP-4 (activating enhancer binding protein 4), transcription factor AP-4 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600743; MGI: 103239; HomoloGene: 2424; GeneCards: TFAP4; OMA:TFAP4 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 16 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 16p13.3 | Start | 4,257,186 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 4,273,075 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 16 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 16 A1|16 2.45 cM | Start | 4,362,525 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 4,377,718 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - olfactory bulb
- beta cell
- vena cava
- sural nerve
- ganglionic eminence
- cerebellar hemisphere
- lateral nuclear group of thalamus
- subthalamic nucleus
- nasal epithelium
- right hemisphere of cerebellum
|
| | Top expressed in | - tail of embryo
- genital tubercle
- ventricular zone
- yolk sac
- epiblast
- female urethra
- muscle of thigh
- lip
- zygote
- embryo
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 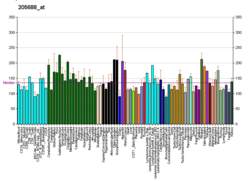 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - sequence-specific DNA binding
- RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- protein homodimerization activity
- protein dimerization activity
- transcription coactivator activity
- histone deacetylase binding
- protein heterodimerization activity
- transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific binding
- DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- protein binding
- DNA binding
- E-box binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
| | Cellular component | - transcription repressor complex
- nucleus
- mitochondrion
| | Biological process | - negative regulation of cell population proliferation
- negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- transcription, DNA-templated
- negative regulation of gene expression
- DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator
- cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus
- negative regulation of DNA binding
- positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway
- positive regulation of apoptotic process
- positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription by RNA polymerase II
- negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition
- protein-containing complex assembly
- regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 16: 4.26 – 4.27 Mb | Chr 16: 4.36 – 4.38 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

















