Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| REST |
|---|
|
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | REST, Rest, 2610008J04Rik, AA407358, NRSF, XBR, REST4, WT6, RE1 silencing transcription factor, GINGF5, HGF5, DFNA27 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600571; MGI: 104897; HomoloGene: 4099; GeneCards: REST; OMA:REST - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 4 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 4q12 | Start | 56,907,876 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 56,966,808 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 5 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 5|5 C3.3 | Start | 77,413,338 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 77,434,279 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - gonad
- mucosa of paranasal sinus
- testicle
- Achilles tendon
- epithelium of nasopharynx
- epithelium of colon
- Epithelium of choroid plexus
- retinal pigment epithelium
- bone marrow cells
- oral cavity
|
| | Top expressed in | - external carotid artery
- internal carotid artery
- zygote
- superior surface of tongue
- cumulus cell
- gallbladder
- human fetus
- secondary oocyte
- primary oocyte
- Gonadal ridge
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - DNA binding
- outward rectifier potassium channel activity
- DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- transcription factor binding
- metal ion binding
- core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding
- protein binding
- nucleic acid binding
- DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- histone deacetylase activity
- chromatin binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding
| | Cellular component | - cytosol
- nucleoplasm
- transcription repressor complex
- nucleus
- cytoplasm
- histone methyltransferase complex
| | Biological process | - cellular response to electrical stimulus
- negative regulation of dense core granule biogenesis
- negative regulation of insulin secretion
- negative regulation of cortisol biosynthetic process
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription by RNA polymerase II
- negative regulation of gene expression
- transcription, DNA-templated
- negative regulation of amniotic stem cell differentiation
- positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- negative regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation
- histone H4 deacetylation
- positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus
- negative regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis
- hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- negative regulation of cell population proliferation
- negative regulation of aldosterone biosynthetic process
- negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- cardiac muscle cell myoblast differentiation
- negative regulation of neurogenesis
- potassium ion transmembrane transport
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- positive regulation of apoptotic process
- negative regulation of neuron differentiation
- regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome
- response to hypoxia
- regulation of gene expression
- positive regulation of neuron differentiation
- regulation of osteoblast differentiation
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001193508
NM_005612
NM_001363453 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001180437
NP_005603
NP_001350382 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 4: 56.91 – 56.97 Mb | Chr 5: 77.41 – 77.43 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
RE1-Silencing Transcription factor (REST), also known as Neuron-Restrictive Silencer Factor (NRSF), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the REST gene, and acts as a transcriptional repressor.[5][6][7] REST is expressly involved in the repression of neural genes in non-neuronal cells.[7][8] Many genetic disorders have been tied to alterations in the REST expression pattern, including colon and small-cell lung carcinomas found with truncated versions of REST.[9] In addition to these cancers, defects in REST have also been attributed a role in Huntington Disease, neuroblastomas, and the effects of epileptic seizures and ischemia.
Function
This gene encodes a transcriptional repressor which represses neuronal genes in non-neuronal tissues. It is a member of the Kruppel-type zinc finger transcription factor family. It represses transcription by binding a DNA sequence element called the neuron-restrictive silencer element (NRSE, also known as RE1). The protein is also found in undifferentiated neuronal progenitor cells, and it is thought that this repressor may act as a master negative regulator of neurogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described; however, their full length nature has not been determined.[5] REST is found to be down-regulated in elderly people with Alzheimer's disease.[10]
REST contains 8 Cys2His2 zinc fingers and mediates gene repression by recruiting several chromatin-modifying enzymes.[11]
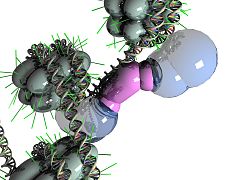
-
NRSF bound to DNA and cofactors on each of its two cofactor binding domains.
-
Chromatin remodeling occurs, causing the gene to be 'turned off'.
REST is also responsible for ischaemia induced neuronal cell death, in mouse models of brain ischaemia. Ischaemia, which results from reduced blood perfusion of tissues, decreasing nutrient and oxygen supply, induces REST transcription and nuclear accumulation, leading to the epigenetic repression of neuronal genes leading to cell death.[12] The mechanism beyond REST induction in ischaemia, might be tightly linked to its oxygen-dependent nuclear translocation and repression of target genes in hypoxia (low oxygen) where REST fulfils the functions of a master regulator of gene repression in hypoxia.[13]
Interactions
RE1-silencing transcription factor has been shown to interact with RCOR1.[14]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000084093 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029249 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: REST RE1-silencing transcription factor".
- ^ Schoenherr CJ, Anderson DJ (March 1995). "The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF): a coordinate repressor of multiple neuron-specific genes". Science. 267 (5202): 1360–3. Bibcode:1995Sci...267.1360S. doi:10.1126/science.7871435. PMID 7871435. S2CID 25101475.
- ^ a b Chong JA, Tapia-Ramírez J, Kim S, Toledo-Aral JJ, Zheng Y, Boutros MC, Altshuller YM, Frohman MA, Kraner SD, Mandel G (March 1995). "REST: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons". Cell. 80 (6): 949–57. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90298-8. PMID 7697725. S2CID 6412634.
- ^ Coulson JM (September 2005). "Transcriptional regulation: cancer, neurons and the REST". Current Biology. 15 (17): R665–8. Bibcode:2005CBio...15.R665C. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.08.032. PMID 16139198. S2CID 11901339.
- ^ Westbrook TF, Martin ES, Schlabach MR, Leng Y, Liang AC, Feng B, Zhao JJ, Roberts TM, Mandel G, Hannon GJ, Depinho RA, Chin L, Elledge SJ (June 2005). "A genetic screen for candidate tumor suppressors identifies REST". Cell. 121 (6): 837–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.033. PMID 15960972. S2CID 14082806.
- ^ Lu T, Aron L, Zullo J, Pan Y, Kim H, Chen Y, Yang TH, Kim HM, Drake D, Liu XS, Bennett DA, Colaiácovo MP, Yankner BA (March 2014). "REST and stress resistance in ageing and Alzheimer's disease". Nature. 507 (7493): 448–54. Bibcode:2014Natur.507..448L. doi:10.1038/nature13163. PMC 4110979. PMID 24670762.
- ^ Ooi L, Wood IC (July 2007). "Chromatin crosstalk in development and disease: lessons from REST". Nature Reviews Genetics. 8 (7): 544–54. doi:10.1038/nrg2100. PMID 17572692. S2CID 415873.
- ^ Noh KM, Hwang JY, Follenzi A, Athanasiadou R, Miyawaki T, Greally JM, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (April 2012). "Repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor (REST)-dependent epigenetic remodeling is critical to ischemia-induced neuronal death". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (16): E962–71. doi:10.1073/pnas.1121568109. PMC 3341013. PMID 22371606.
- ^ Cavadas MA, Mesnieres M, Crifo B, Manresa MC, Selfridge AC, Keogh CE, Fabian Z, Scholz CC, Nolan KA, Rocha LM, Tambuwala MM, Brown S, Wdowicz A, Corbett D, Murphy KJ, Godson C, Cummins EP, Taylor CT, Cheong A (17 Aug 2016). "REST is a hypoxia-responsive transcriptional repressor". Scientific Reports. 6: 31355. Bibcode:2016NatSR...631355C. doi:10.1038/srep31355. PMC 4987654. PMID 27531581.
- ^ Andrés ME, Burger C, Peral-Rubio MJ, Battaglioli E, Anderson ME, Grimes J, Dallman J, Ballas N, Mandel G (August 1999). "CoREST: a functional corepressor required for regulation of neural-specific gene expression". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (17): 9873–8. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.9873A. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.17.9873. PMC 22303. PMID 10449787.
Further reading
- Ooi L, Wood IC (July 2007). "Chromatin crosstalk in development and disease: lessons from REST". Nature Reviews Genetics. 8 (7): 544–54. doi:10.1038/nrg2100. PMID 17572692. S2CID 415873.
- Chong JA, Tapia-Ramírez J, Kim S, Toledo-Aral JJ, Zheng Y, Boutros MC, Altshuller YM, Frohman MA, Kraner SD, Mandel G (March 1995). "REST: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons". Cell. 80 (6): 949–57. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90298-8. PMID 7697725. S2CID 6412634.
- Schoenherr CJ, Anderson DJ (March 1995). "The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF): a coordinate repressor of multiple neuron-specific genes". Science. 267 (5202): 1360–3. Bibcode:1995Sci...267.1360S. doi:10.1126/science.7871435. PMID 7871435. S2CID 25101475.
- Scholl T, Stevens MB, Mahanta S, Strominger JL (February 1996). "A zinc finger protein that represses transcription of the human MHC class II gene, DPA". Journal of Immunology. 156 (4): 1448–57. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.156.4.1448. PMID 8568247.
- Coulson JM (September 2005). "Transcriptional regulation: cancer, neurons and the REST". Current Biology. 15 (17): R665–8. Bibcode:2005CBio...15.R665C. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.08.032. PMID 16139198. S2CID 11901339.
- Thiel G, Lietz M, Cramer M (October 1998). "Biological activity and modular structure of RE-1-silencing transcription factor (REST), a repressor of neuronal genes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (41): 26891–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.41.26891. PMID 9756936.
- Andrés ME, Burger C, Peral-Rubio MJ, Battaglioli E, Anderson ME, Grimes J, Dallman J, Ballas N, Mandel G (August 1999). "CoREST: a functional corepressor required for regulation of neural-specific gene expression". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (17): 9873–8. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.9873A. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.17.9873. PMC 22303. PMID 10449787.
- Palm K, Metsis M, Timmusk T (September 1999). "Neuron-specific splicing of zinc finger transcription factor REST/NRSF/XBR is frequent in neuroblastomas and conserved in human, mouse and rat". Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research. 72 (1): 30–9. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(99)00196-5. PMID 10521596.
- Naruse Y, Aoki T, Kojima T, Mori N (November 1999). "Neural restrictive silencer factor recruits mSin3 and histone deacetylase complex to repress neuron-specific target genes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (24): 13691–6. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9613691N. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.24.13691. PMC 24126. PMID 10570134.
- Grimes JA, Nielsen SJ, Battaglioli E, Miska EA, Speh JC, Berry DL, Atouf F, Holdener BC, Mandel G, Kouzarides T (March 2000). "The co-repressor mSin3A is a functional component of the REST-CoREST repressor complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (13): 9461–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.13.9461. PMID 10734093.
- Coulson JM, Edgson JL, Woll PJ, Quinn JP (April 2000). "A splice variant of the neuron-restrictive silencer factor repressor is expressed in small cell lung cancer: a potential role in derepression of neuroendocrine genes and a useful clinical marker". Cancer Research. 60 (7): 1840–4. PMID 10766169.
- Kojima T, Murai K, Naruse Y, Takahashi N, Mori N (June 2001). "Cell-type non-selective transcription of mouse and human genes encoding neural-restrictive silencer factor". Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research. 90 (2): 174–86. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(01)00107-3. PMID 11406295.
- Battaglioli E, Andrés ME, Rose DW, Chenoweth JG, Rosenfeld MG, Anderson ME, Mandel G (October 2002). "REST repression of neuronal genes requires components of the hSWI.SNF complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (43): 41038–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205691200. PMID 12192000.
- Lunyak VV, Burgess R, Prefontaine GG, Nelson C, Sze SH, Chenoweth J, Schwartz P, Pevzner PA, Glass C, Mandel G, Rosenfeld MG (November 2002). "Corepressor-dependent silencing of chromosomal regions encoding neuronal genes". Science. 298 (5599): 1747–52. Bibcode:2002Sci...298.1747L. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.136.7131. doi:10.1126/science.1076469. PMID 12399542. S2CID 13507921.
- Lietz M, Hohl M, Thiel G (January 2003). "RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST) regulates human synaptophysin gene transcription through an intronic sequence-specific DNA-binding site". European Journal of Biochemistry. 270 (1): 2–9. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03360.x. PMID 12492469.
- Hersh LB, Shimojo M (March 2003). "Regulation of cholinergic gene expression by the neuron restrictive silencer factor/repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor". Life Sciences. 72 (18–19): 2021–8. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00065-1. PMID 12628452.
- Kemp DM, Lin JC, Habener JF (September 2003). "Regulation of Pax4 paired homeodomain gene by neuron-restrictive silencer factor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (37): 35057–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305891200. PMID 12829700.
- Zuccato C, Tartari M, Crotti A, Goffredo D, Valenza M, Conti L, Cataudella T, Leavitt BR, Hayden MR, Timmusk T, Rigamonti D, Cattaneo E (September 2003). "Huntingtin interacts with REST/NRSF to modulate the transcription of NRSE-controlled neuronal genes". Nature Genetics. 35 (1): 76–83. doi:10.1038/ng1219. PMID 12881722. S2CID 28110381.
- Martin D, Tawadros T, Meylan L, Abderrahmani A, Condorelli DF, Waeber G, Haefliger JA (December 2003). "Critical role of the transcriptional repressor neuron-restrictive silencer factor in the specific control of connexin36 in insulin-producing cell lines". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (52): 53082–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306861200. PMID 14565956.
- Kuwahara K, Saito Y, Takano M, Arai Y, Yasuno S, Nakagawa Y, Takahashi N, Adachi Y, Takemura G, Horie M, Miyamoto Y, Morisaki T, Kuratomi S, Noma A, Fujiwara H, Yoshimasa Y, Kinoshita H, Kawakami R, Kishimoto I, Nakanishi M, Usami S, Saito Y, Harada M, Nakao K (December 2003). "NRSF regulates the fetal cardiac gene program and maintains normal cardiac structure and function". The EMBO Journal. 22 (23): 6310–21. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg601. PMC 291842. PMID 14633990.
- Kuwabara T, Hsieh J, Nakashima K, Taira K, Gage FH (March 2004). "A small modulatory dsRNA specifies the fate of adult neural stem cells". Cell. 116 (6): 779–93. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00248-X. PMID 15035981. S2CID 12656737.
- Zullo JM, Drake D, Aron L, O'Hern P, Dhamne SC, Davidsohn N, Mao CA, Klein WH, Rotenberg A, Bennett DA, Church GM, Colaiácovo MP, Yankner BA (October 2019). "Regulation of lifespan by neural excitation and REST". Nature. 574 (7778): 359–364. Bibcode:2019Natur.574..359Z. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1647-8. PMC 6893853. PMID 31619788.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
(1) Basic domains |
|---|
| (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) | |
|---|
| (1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) | | Group A | |
|---|
| Group B | |
|---|
Group C
bHLH-PAS | |
|---|
| Group D | |
|---|
| Group E | |
|---|
Group F
bHLH-COE | |
|---|
|
|---|
| (1.3) bHLH-ZIP | |
|---|
| (1.4) NF-1 | |
|---|
| (1.5) RF-X | |
|---|
| (1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH) | |
|---|
|
|
(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains |
|---|
| (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4) | | subfamily 1 | |
|---|
| subfamily 2 | |
|---|
| subfamily 3 | |
|---|
| subfamily 4 | |
|---|
| subfamily 5 | |
|---|
| subfamily 6 | |
|---|
| subfamily 0 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| (2.2) Other Cys4 | |
|---|
| (2.3) Cys2His2 | |
|---|
| (2.4) Cys6 | |
|---|
| (2.5) Alternating composition | |
|---|
| (2.6) WRKY | |
|---|
|
|
|
(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts |
|---|
|
|
(0) Other transcription factors |
|---|
|
|
see also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies |
 NRSF bound to DNA and cofactors on each of its two cofactor binding domains.
NRSF bound to DNA and cofactors on each of its two cofactor binding domains.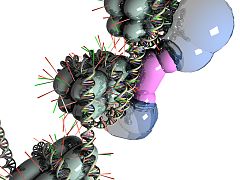 Chromatin remodeling occurs, causing the gene to be 'turned off'.
Chromatin remodeling occurs, causing the gene to be 'turned off'.





















